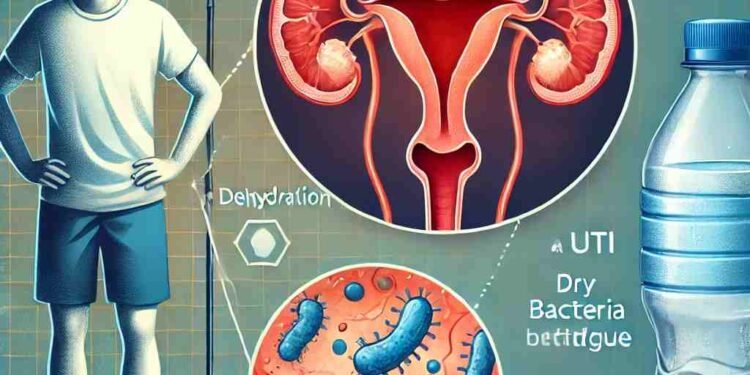
Yes, dehydration can indeed increase the risk of urinary tract infections (UTIs). The connection between dehydration and UTIs might not be immediately obvious, but staying properly hydrated plays a crucial role in preventing these infections.
In my experience, dehydration can make you more likely to get a UTI. When I don’t drink enough water, I’ve noticed I feel uncomfortable, and my body doesn’t flush out waste as well. This can let bacteria build up in the urinary tract.
I remember a time when I wasn’t drinking enough and felt some discomfort when peeing. After I started drinking more water, I felt better. Now, I make sure to stay hydrated to keep my urinary system healthy and avoid any issues like UTIs.
Understanding UTIs:
A urinary tract infection is an infection in any part of the urinary system, including the kidneys, bladder, ureters, and urethra. The most common cause of UTIs is bacteria, particularly Escherichia coli (E. coli), which can enter the urinary tract through the urethra. UTIs often lead to symptoms like painful urination, frequent urination, cloudy urine, and lower abdominal pain.
How Dehydration Contributes to UTIs?
Reduced Urine Flow:
When you’re dehydrated, your body produces less urine. This means that bacteria in the urinary tract have less urine to flush them out, increasing the risk of infection. A healthy urinary flow helps prevent bacterial buildup by naturally washing out microorganisms before they have a chance to cause harm.
Concentrated Urine:
Dehydration leads to more concentrated urine, which can irritate the urinary tract and create a favorable environment for bacteria to grow. A more acidic environment in the bladder, combined with the slower flow of urine, can increase the likelihood of bacteria thriving.
Decreased Bladder Emptying:
Dehydration may also make it harder for the bladder to fully empty during urination. This can leave behind traces of urine where bacteria can multiply, increasing the chances of infection.
Prevention and Treatment:
To lower the risk of developing a UTI due to dehydration, it’s essential to stay properly hydrated by drinking sufficient amounts of water throughout the day. The general recommendation is to drink around 8 glasses (64 ounces) of water daily, but individual needs may vary based on factors like age, activity level, and climate.
If you experience symptoms of a UTI, it’s important to seek medical advice for treatment. UTIs are typically treated with antibiotics to eliminate the bacteria causing the infection. In cases of recurrent UTIs or dehydration-related issues, healthcare providers may offer tailored advice on preventing further occurrences.
Two warning signs of dehydration are:
- Dark yellow, strong-smelling urine – This indicates that your body is not getting enough water, and your urine becomes more concentrated.
- Dizziness or lightheadedness – Dehydration can reduce fluid levels in your body, affecting circulation and causing you to feel dizzy or faint.
Other symptoms include thirst, peeing less often, feeling tired, dry mouth, lips, and tongue, and sunken eyes.
Impact of Dehydration on UTI Symptoms:
In addition to increasing the risk of developing a UTI, dehydration can worsen the symptoms of an existing infection. When the body is dehydrated, the frequency of urination decreases, which allows bacteria to linger in the urinary tract for longer periods. This extended exposure increases the likelihood of the bacteria multiplying and spreading, potentially leading to more severe symptoms and complications.
The Role of Hydration in UTI Prevention:
Maintaining proper hydration is one of the most straightforward ways to help prevent UTIs. Drinking an adequate amount of water throughout the day ensures that urine stays diluted and can be easily flushed out from the body, reducing the likelihood of bacterial buildup. It’s also beneficial for individuals who are prone to recurrent UTIs or those who have a history of urinary tract issues.
FAQs:
1. Can dehydration cause a UTI?
Yes, dehydration can increase the risk of developing a UTI because it reduces the amount of urine, which helps flush out bacteria.
2. How much water should I drink to prevent a UTI?
Drinking about 8 glasses of water a day can help prevent UTIs by keeping your urinary system flushed and hydrated.
3. Does dehydration make a UTI worse?
Yes, dehydration can make UTI symptoms like pain and discomfort worse by concentrating urine, which irritates the bladder.
4. Are women more at risk of UTIs from dehydration than men?
Yes, women are more likely to get UTIs due to dehydration because their urethras are shorter, making it easier for bacteria to enter.
5. Can dehydration lead to kidney infections?
Yes, if a UTI is left untreated and dehydration makes it harder to flush out bacteria, it can spread to the kidneys and cause an infection.
Conclusion:
In summary, dehydration can increase the risk of developing UTIs by allowing bacteria to thrive in a more concentrated urinary environment. Staying well-hydrated is a simple yet effective way to lower the risk of UTIs, promote urinary health, and improve overall well-being. Make sure to drink enough fluids each day, especially water, to help maintain a healthy urinary system and prevent unnecessary infections.
Also Read:








Discussion about this post